ROSS ISLAND
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Update frequencies
status
-

Ultraviolet radiation measurements over the spectral region 290-450 nm with a high precision spectro-radiometer. The spectro-radiometer was installed at Arrival Heights as a two month (November 2006 – January 2007) blind inter-comparison with the established measurement programme run by Biospherical Instruments for the USAP. The data was compared with the USAP data taken simultaneously. These data are held internally by NIWA. GET DATA: contact dan.smale@niwa.co.nz
-
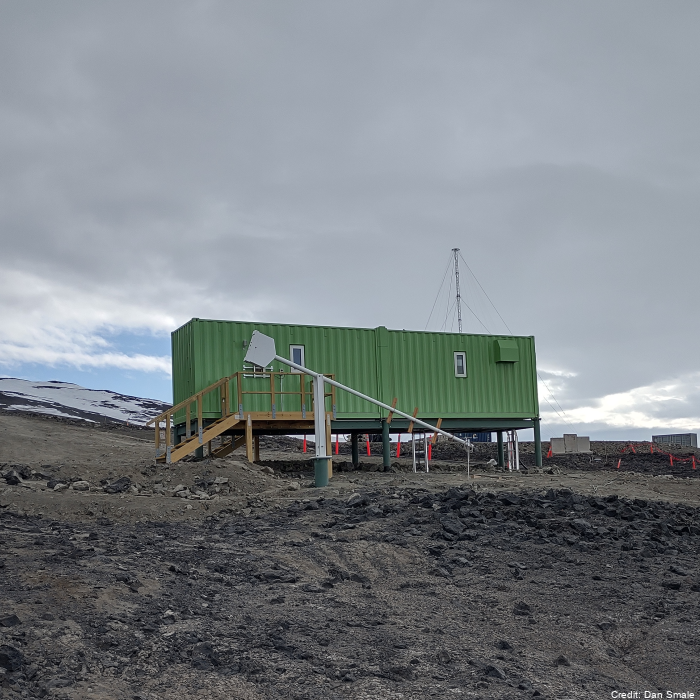

Measurements of chlorine monoxide (ClO) made with a Microwave Chlorine Monoxide Millimeter Wave Spectrometer (ground-based). The instrument (ClOe1) was established in January of 1996 at Scott Base and decommissioned in October 2023. A replacement radiometer (ClOe4) was installed at Scott Base in February 2023 (an overlap in the data for timeseries continuity purposes). These data are produced in collaboration with State University of New York (SUNY) Stoney Brook and Naval Research Laboratory (NRL). “Raw” data are times and recorded microwave emission spectra. “Derived” data are column amounts and vertical profile information of chlorine monoxide (ClO). The instrument has acquired the nickname "CloeTechnique" for vertical profile information uses "optimal estimation" to extract information from pressure broadening of ClO emission line. Significant failure in early 2018 only fixed in November 2018. No data in the July - October 2018 period. Data is held at NRL and in the NDACC database. Data are available as monthly .ndm files, and additional metadata are available in the header. Instrument timeline: - ClOe1 1996-2023 - ClOe4 2023 – present GET DATA: https://www-air.larc.nasa.gov/missions/ndacc/data.html?station=scott.base#
-

The WWLLN Very Low Frequency (VLF) Radio Sensor was installed at Scott Base in November 2015 by Dr. James Brundell and Ms. Emma Douma as part of Antarctica New Zealand Event K060-1516-A. The sensor measures the electric field in the Very Low Frequency radio range (~500 Hz-50 kHz) and passes it to a PC which processes the data for the experiments. The antenna is located behind the Hatherton lab. It was installed due to increasing manmade electromagnetic noise levels in the "quiet zone" at Arrival Heights. The observations from this antenna are now the primary WWLLN feed from Ross Island, the Arrival Height's magnetic field antenna is now a backup. WWLLN, uses the VLF feed but processes it to detect the radio-wave pulses from lightning. WWLLN observations are sent to a central processing computer to determine the time and location of lightning pulses all over the globe. The World Wide Lightning Location Network (WWLLN) is an experimental Very Low Frequency (VLF) network of sensors being developed through collaborations with research institutions across the globe. The network exploits the considerable electromagnetic power radiated by lightning as "sferics" present in the VLF band. By combining radio-pulse observations from at least 5 stations, the WWLLN central processing computers can determine the location of the original lightning discharge. As the radio-pulse observations are immediately sent back across the internet to the central processing computers locations are generated within ~10 s of the discharge, and thus near real time. There are currently about 70 active VLF receiving stations operating in the VLF World-Wide Lightning Location Network, including the Scott Base measurements. WWLLN observations are continuously transmitted to one of the WWLLN primary servers, in this case flash.ess.washington.edu at the University of Washington, Seattle, USA. GET DATA: https://space.physics.otago.ac.nz/aarddvark/
-
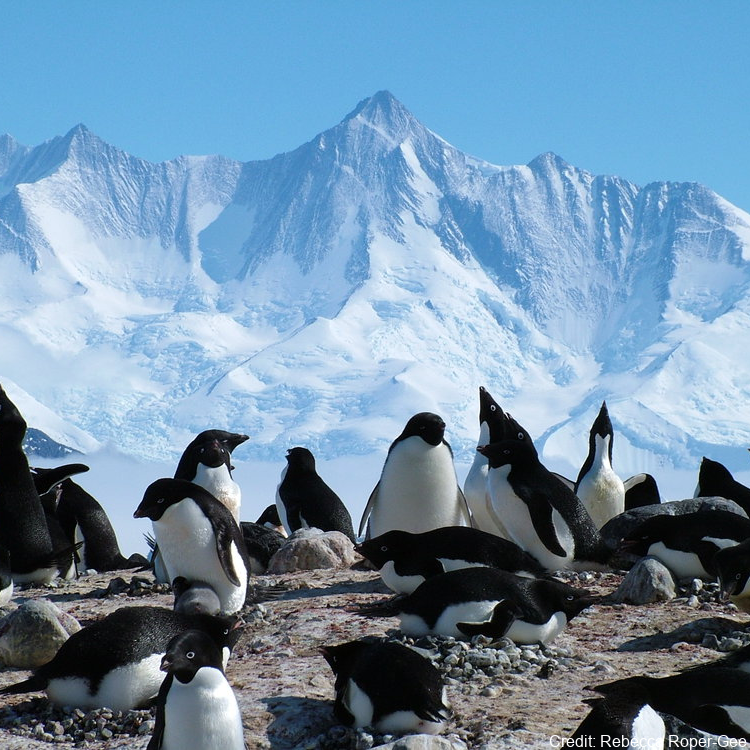

Polar regions are experiencing some of the most dramatic effects of climate change resulting in large-scale changes in sea ice cover. Despite this, there are relatively few long-term studies on polar species that evaluate the full scope of these effects. Over the last two decades, this team has conducted globally unique demographic studies of Adélie penguins in the Ross Sea, Antarctica, to explore several potential mechanisms for population change. This five-year project will use penguin-borne sensors to evaluate foraging conditions and behavior and environmental conditions on early life stages of Adélie penguins. Results will help to better understand population dynamics and how populations might respond to future environmental change. To promote STEM literacy, education and public outreach efforts will include multiple activities. The PenguinCam and PenguinScience.com website (impacts of >1 million hits per month and use by >300 classrooms/~10,000 students) will be continued. Each field season will also have ‘Live From the Penguins’ Skype calls to classes (~120/season). Classroom-ready activities that are aligned with Next Generation Science Standards will be developed with media products and science journal papers translated to grade 5-8 literacy level. The project will also train early career scientists, postdoctoral scholars, graduate students and post-graduate interns. Finally, in partnership with an Environmental Leadership Program, the team will host 2-year Roger Arliner Young Conservation Fellow, which is a program designed to increase opportunities for recent college graduates of color to learn about, engage with, and enter the environmental conservation sector. Further details are provided at: Morandini, V., Dugger, K. M., Schmidt, A. E., Varsani, A., Lescroël, A., Ballard, G., Lyver, P. O., Barton, K., & Ainley, D. G. (2024). Sex-specific recruitment rates contribute to male-biased sex ratio in Adélie penguins. Ecology and Evolution, 14, e10859. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.10859 GET DATA: https://doi.org/10.15784/601444
-
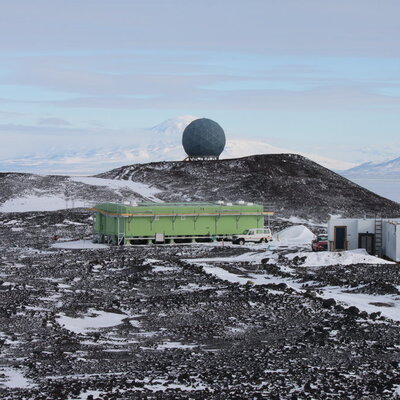

Measurements of total column of ozone made with Dobson spectrophotometer that measures either direct or zenith scattered ultraviolet light. The instrument was established in September of 1989 at 77° 49.8'S, 166° 39.6'E. Additionally a Brewer spectrophotometer took total column ozone measurements at Scott from 1989 to 1996. From 1989 to 2006 the Dobson (ID 17) was operated in manual mode but had an electronic encoder and computer added in 2006 for recording measurements. The data acquisition system was upgraded in Febuerary 2015 at Lauder, NZ. It is now running the JMA automation system. The Dobson (instrument ID: D17) is shipped out for maintenance and intercomparison with regional standard Dobson in Melbourne approximately every 5 years. Data (for both Dobson and Brewer) is held internally by NIWA and in the NDACC database. Data is also archived in the ozone and UV data centre Toronto, “Raw” data are times and instrument settings for instrument readings. “Derived” data are column amounts of ozone. Time line: Dobson 1987 -present Brewer 1989-1996 GET DATA: https://www-air.larc.nasa.gov/missions/ndacc/data.html?station=arrival.heights#
-
Here we examine the water stable-isotope data from the Roosevelt Island Climate Evolution (RICE) ice core. In this study, we use empirical orthogonal function (EOF) analysis to investigate the relationship between RICE ice-core oxygen-18 isotopes (δ18O) and Southern Hemisphere atmospheric circulation during the extended austral winter (April–November). - Deep Location: 79.364°S, 161.706°W, elevation 550 m a.s.l. - 12/13B Location: 79.362°S, 161.698°W, elevation 550 m a.s.l. - Core depth 763 m. Depth interval provided here: 1.29 to 38.56 m - txt data file, NaN = no data Further details are available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06568-8 GET DATA: https://github.com/demanuelsson/ClimDyn_2022_Matlab/tree/main/data
-

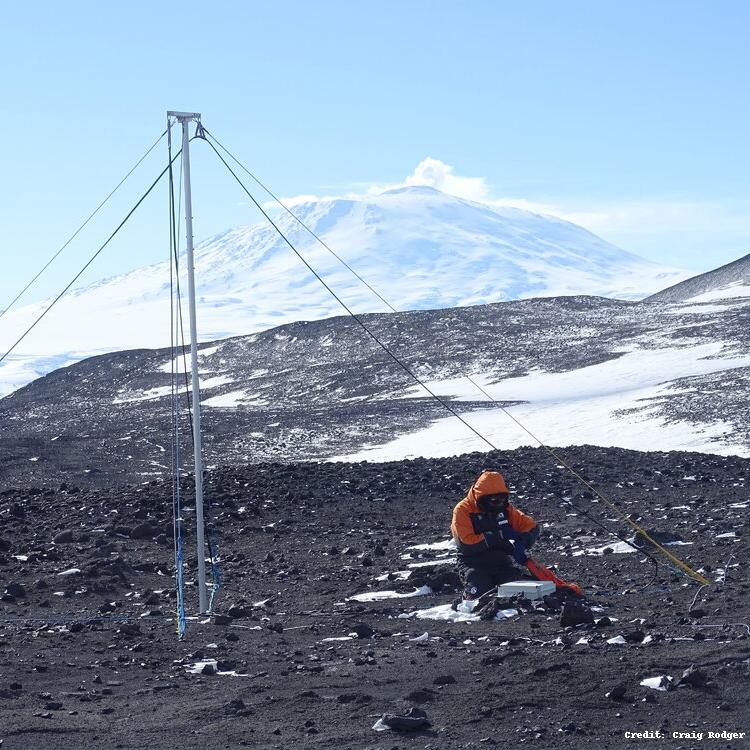
The AARDDVARK/WWLLN Very Low Frequency (VLF) Radio Sensor was installed at Arrival Heights from 10-15 December 2008 by Dr Craig J. Rodger and Dr. James Brundell as part of Antarctica New Zealand Event K069A. The sensor measures the magnetic field in the Very Low Frequency radio range (~500 Hz-50 kHz), and passes it to a PC which processes the data for the experiments. The primary experiment is the AARDDVARK observations, which measures powerful and distant communications transmitters operating in the VLF range. As such, the dataset is "narrowband", taking amplitude and phase measurements at the transmission frequencies. For this sensor, there is 0.2s time resolution. The Konsortia sensors detect changes in ionisation levels from ~30-85 km altitude, with the goal of increasing the understanding of energy coupling between the Earth's atmosphere, Sun, and Space. We use the upper atmosphere as a gigantic energetic particle detector to observe and understand changing energy flows; this Science area impacts our knowledge of global change, communications, and navigation. One of the few experimental techniques that can probe these altitudes uses very low-frequency (VLF) electromagnetic radiation, trapped between the lower ionosphere (~85 km) and the Earth, and thus said to be propagating "subionospherically". The sensor is currently logging transmitters in the northern & southern hemispheres, over a very wide longitude range. Both experiments send the processed data across the internet. AARDDVARK observations are sent to the University of Otago once a day at an agreed time. The new AH receiver was the 10th station in the AARDDVARK network, jointly lead by the University of Otago and the British Antarctic Survey. Two near-orthogonal magnetic field loops measuring VLF electromagnetic waves. The centre of the antenna is at 77° 49.790' S, 166° 39.438' E, based on a GPS measurement with 1 m accuracy. Logging is undertaken with UltraMSK software running on a PC locked to GPS timing. GET DATA: https://space.physics.otago.ac.nz/aarddvark/
-
Spectroscopic measurements of stratospheric gases Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2), Chlorine Dioxide (OCIO), Bromine Oxide (BrO) and Ozone (O3) using scattered sunlight. Airyx and Envimeas: A dual MAX-DOAS UV/visible wavelength diode array spectrometer is deployed to measure of ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), chlorine dioxide (OClO) and bromine oxide (BrO). The instrument is a similar instrument to that of EnviMeas, and produces overlapping datasets with ADAS-2. Fixed azimuth direction, same as the Antarctic Diode Array spectrometer. System 2 (ADAS-2). The data are currently being held internally by NIWA. “Raw” data are times and recorded spectra of scattered light for several viewing directions. “Derived” data are column amount of NO2, OClO, BrO and O3, which can be split into tropospheric and stratospheric parts. This technique is sometimes referred to as MAX-DOAS Multiple-Axis Dual Optical Absorption Spectrometry. This work is carried out in collaboration the University of Heidelberg. ADAS2, Envimeas and Airyx measurements: UV/visible Multi-Axis Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS) diode array spectrometers making measurements of ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), chlorine dioxide (OClO) and bromine oxide (BrO). JY: A scanning grating UV/Vis monochromator taking measurements of total slant column of NO2 and Ozone using scattered zenith sunlight. ADAS: A CCD grating UV/Vis grating Acton spectrometer making measurements of total slant column NO2, BrO, OClO and ozone made using scattered light zenith sunlight. Pandora: Direct sun UV/Vis measurements of ozone and NO2. Campaign to test feasibility of long term deployment at Arrival Heights. Instrument timeline JY: 1982 -2023 ADAS: 1993 - 2017 ADAS2: 1998 - present Pandora: 2015 Aug – Oct. Airyx & Envimeas : 2018 – present O3, OCIO and BrO data are in the process of being archived - please contact Richard Querel for data access. NO2 data is available via the "GET DATA" link. GET DATA: https://www-air.larc.nasa.gov/missions/ndacc/data.html?station=arrival.heights
-

Measurements of boundary layer concentration of ozone are made with insitu instruments that samples air continuously at Arrival Heights, Antarctica and is part of the NOAA Global Monitoring Surface Ozone Network. Original measurements at Arrival Heights were made with a Dasibi Environmental Corp in situ analyser. This was replaced with a TEI-49c in situ analyser. The TEI-49c is owned by NOAA and operated by NIWA at Arrival Heights until October 2023. In October 2023 operation of the TEI was transferred to the USAP Arrival Heights laboratory along with operational responsibility (between NOAA and USAP). This data set contains continuous UV photometric data of surface level ozone collected at 6m above ground level. Data records consist of UTC time, date, and processed ozone mixing ratio (parts per billion). Data is collected from global locations and is provided in 1 minute and 1 hour averages. Data are archived at the NOAA National Climatic Data Center (NCDC), but are produced and available from NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory (ESRL). Instrument timeline: - Dasibi 1997-2003 - TEI49c 2003 – October 2023 - TEI49i November 2023 -present at USAP Arrival Heights laboratory GET DATA: https://gml.noaa.gov/aftp/data/ozwv/SurfaceOzone/ARH/
-
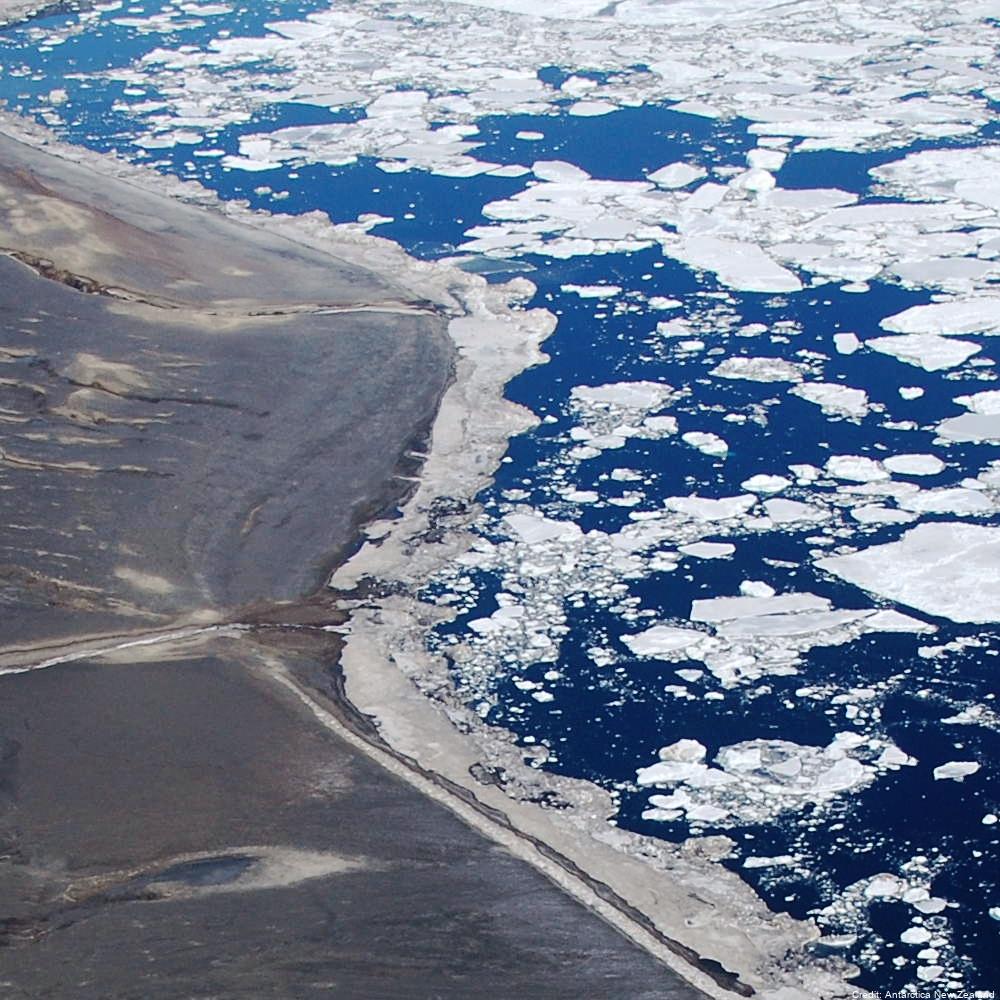

Aerial reconnaissance and photography are used in the Ross Sea sector of Antarctica to determine the breeding locations of Adélie penguins and to count the numbers of nests occupied during the early incubation period. From 1981 to present (two-year embargo), all islands and sea coasts between 158°E and 175°E have been searched, and 11 previously unreported breeding colonies discovered. The aim is to census Adélie (Pygoscelis adeliae) populations to provide basic data against which future population levels can be compared in order to monitor environmental change of the Antarctic Ocean ecosystem, both natural and man-induced. GET DATA: https://datastore.landcareresearch.co.nz/en_AU/dataset/adelie-penguin-census-data
 Metadata Catalogue
Metadata Catalogue